What is a good credit score for business takes center stage as we delve into the world of business financing. Understanding your credit score is crucial for securing loans, attracting investors, and building a strong financial foundation for your company. This guide explores the intricacies of business credit scores, shedding light on the factors that influence them and the benefits of maintaining a healthy score.
In the realm of business, a good credit score acts as a beacon, signaling to lenders and investors that your company is financially responsible and trustworthy. It’s a numerical representation of your business’s financial health, reflecting your payment history, debt levels, and overall creditworthiness.
Understanding Credit Scores: What Is A Good Credit Score For Business

A business credit score is a crucial factor in securing funding and establishing financial credibility. Lenders use this score to assess the risk associated with lending money to your business. A higher credit score indicates a lower risk, which can lead to better interest rates and more favorable loan terms.
Credit Scoring Models
Different credit scoring models are used to evaluate the creditworthiness of businesses. These models take into account various factors and may vary depending on the lender or credit bureau. Some common models include:
- FICO Small Business Scoring Service (SBSS): This model is widely used by lenders and is based on data from Dun & Bradstreet (D&B). It considers factors such as payment history, debt levels, and financial stability.
- Paydex: Developed by D&B, Paydex measures a business’s payment performance on timeliness and consistency. It is a key component of the D&B credit score.
- Equifax Small Business Credit Risk Score: This model assesses the risk associated with lending to small businesses based on their credit history, financial performance, and industry trends.
Factors Affecting Business Credit Scores
Several factors influence a business credit score. These include:
- Payment History: Timely payments on all business obligations, including loans, credit cards, and utilities, are crucial for a good credit score. Late or missed payments can significantly damage your credit rating.
- Debt Levels: The amount of debt your business has relative to its income, known as the debt-to-income ratio, is a key factor in credit scoring. A higher debt-to-income ratio can indicate a higher risk to lenders.
- Credit Utilization: This refers to the amount of available credit your business is using. A high credit utilization ratio can negatively impact your score, as it suggests you are heavily reliant on credit.
- Length of Credit History: A longer credit history, demonstrating a consistent track record of responsible credit management, generally leads to a higher score.
- Credit Mix: Having a diverse mix of credit accounts, such as business loans, credit cards, and lines of credit, can demonstrate financial responsibility and contribute to a better score.
- Public Records: Any negative public records, such as bankruptcies or judgments, can significantly affect your business credit score.
- Business Size and Industry: The size and industry of your business can also influence your credit score. Certain industries may be perceived as riskier than others.
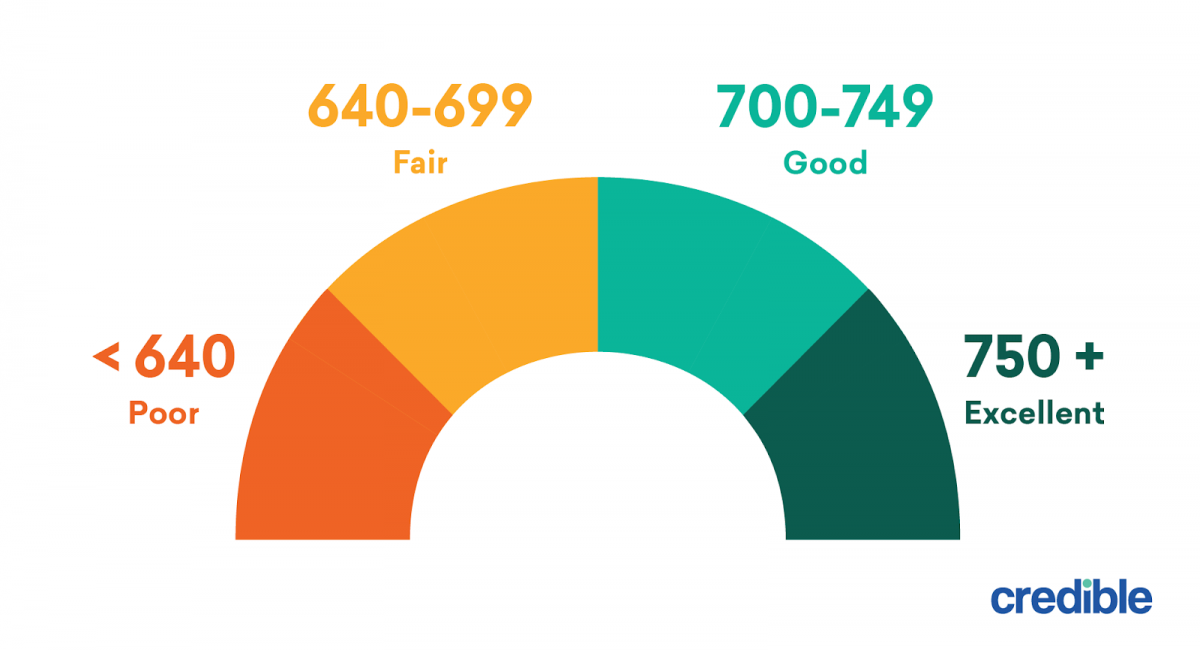
Good Credit Score Ranges for Businesses
A good credit score for a business is essential for securing loans, obtaining favorable financing terms, and attracting investors. It reflects a company’s financial health and ability to manage debt responsibly.
Credit Score Ranges for Businesses
The credit score ranges considered good for businesses vary depending on the lender, the industry, and the business size. However, a general guideline is that a score of 700 or above is typically considered good. Scores below 700 may indicate higher risk to lenders and may result in less favorable terms.
Credit Score Requirements for Different Lenders, What is a good credit score for business
- Small Business Administration (SBA) Loans: The SBA generally requires a credit score of at least 680 for most loan programs. However, specific requirements may vary depending on the loan type and the lender. For example, the SBA 7(a) loan program, which is the most common SBA loan program, has a minimum credit score requirement of 640.
- Commercial Banks: Commercial banks often have stricter credit score requirements than the SBA. They typically require a credit score of at least 700, and some may even require a score of 750 or higher. This is because commercial banks are typically more risk-averse than the SBA. They are also more likely to lend to larger businesses with a longer track record.
- Online Lenders: Online lenders often have more flexible credit score requirements than traditional lenders. They may be willing to lend to businesses with credit scores as low as 600. However, it is important to note that online lenders typically charge higher interest rates than traditional lenders. This is because they are taking on more risk by lending to businesses with lower credit scores.
Benefits of a Good Credit Score
A good credit score is a valuable asset for any business. It opens doors to opportunities that can significantly contribute to a company’s growth and success. By demonstrating financial responsibility and a track record of timely payments, businesses can unlock a range of benefits that can propel them forward.
Impact on Securing Loans
A good credit score is crucial for securing loans. Lenders view it as a reliable indicator of a borrower’s ability to repay borrowed funds. Businesses with strong credit scores are more likely to be approved for loans, as lenders perceive them as lower risk. This access to capital can be instrumental in funding expansion, purchasing new equipment, or managing cash flow during challenging periods.
Advantages in Interest Rates and Loan Terms
Having a good credit score translates to favorable interest rates and loan terms. Lenders reward businesses with strong credit by offering lower interest rates, which can significantly reduce the overall cost of borrowing. This can free up more capital for investment and growth. Additionally, businesses with good credit scores may qualify for longer loan terms, providing more flexibility in repayment and easing financial pressure.
Improved Reputation and Attracting Investors
A good credit score enhances a business’s reputation and makes it more attractive to investors. A strong credit history signals financial stability and responsible management practices, which can inspire confidence in potential investors. When businesses demonstrate financial discipline, they become more appealing to lenders, investors, and even customers, as it reflects a commitment to reliability and trustworthiness.
Improving Business Credit Score
Building and maintaining a good credit score is crucial for any business. A strong credit score allows your business to access better financing options, secure lower interest rates, and build trust with potential partners. It is essential to have a plan in place to improve your business credit score, which can take time and effort.
Strategies for Managing Debt and Improving Payment History
Managing debt and improving payment history are critical components of boosting your business credit score.
- Pay Bills on Time: The most significant factor influencing your business credit score is your payment history. Make sure to pay all your bills on time, including utility bills, rent, and loan payments. Late payments can severely impact your score.
- Reduce Debt Levels: High debt levels can negatively affect your credit score. Consider strategies like debt consolidation or paying down high-interest debt first to improve your score.
- Avoid New Debt: Before taking on new debt, carefully assess your business’s ability to manage it. Avoid opening new credit lines or incurring additional debt unless absolutely necessary.
Building a Strong Credit History by Establishing Trade Lines
Establishing trade lines is a crucial step in building a strong credit history for your business.
- Open a Business Credit Card: Business credit cards can help establish trade lines and improve your credit score. Use the card responsibly and pay your balance in full each month to avoid interest charges.
- Apply for Business Loans: Applying for and obtaining business loans, even small ones, can help establish trade lines. Make sure to shop around for the best interest rates and terms.
- Utilize Trade Credit: Trade credit is a form of financing offered by suppliers to businesses. Paying trade credit accounts on time can help build a positive payment history and establish trade lines.
Impact of Credit Score on Business Operations
A poor credit score can significantly impact a business’s operations, hindering its growth and overall success. A low credit score can lead to higher borrowing costs, limited access to funding, and strained relationships with suppliers, ultimately affecting the business’s ability to compete and thrive in the market.
Consequences of a Poor Credit Score
A low credit score can have far-reaching consequences for a business, impacting its ability to secure financing, negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, and even attract new customers. Here are some of the key consequences:
- Higher Interest Rates on Loans: Lenders perceive businesses with low credit scores as higher risk and therefore charge higher interest rates on loans. This can significantly increase the cost of borrowing, reducing profitability and hindering growth.
- Limited Access to Funding: Many lenders have minimum credit score requirements for approving loans. Businesses with poor credit scores may find it difficult to secure loans from traditional banks and may have to rely on alternative financing options, which often come with higher interest rates and stricter terms.
- Supplier Payment Delays: Suppliers may be hesitant to extend credit to businesses with poor credit scores, leading to delays in receiving supplies and potential disruptions to operations.
- Negative Impact on Business Reputation: A poor credit score can damage a business’s reputation and make it difficult to attract new customers and investors.
Hindered Growth and Expansion
A low credit score can significantly impede a business’s growth and expansion plans. For instance, a company seeking to expand its operations may need to secure a loan to finance new equipment or facilities. However, a poor credit score could prevent them from obtaining the necessary funding, effectively halting their growth plans.
Impact on Supplier Relationships and Access to Resources
A poor credit score can strain relationships with suppliers, making it difficult to secure favorable terms or even obtain supplies. Suppliers may be hesitant to extend credit to businesses with a low credit score, requiring businesses to pay upfront or face delays in receiving supplies. This can lead to disruptions in production, delays in fulfilling orders, and ultimately damage a business’s reputation. Additionally, businesses with poor credit scores may have difficulty accessing other essential resources, such as insurance or leasing agreements, further limiting their ability to operate effectively.
Ultimate Conclusion

Ultimately, a good credit score is an invaluable asset for any business. It opens doors to favorable loan terms, attracts investors, and enhances your company’s reputation. By diligently managing your business’s finances and prioritizing credit health, you can pave the way for sustained growth and success.
FAQ Overview
How do I check my business credit score?
You can obtain your business credit score from credit reporting agencies like Dun & Bradstreet, Experian, and Equifax. These agencies provide reports and scores specifically tailored for businesses.
What are the consequences of a poor credit score for my business?
A poor credit score can make it challenging to secure loans, leading to higher interest rates and limited financing options. It can also affect your ability to obtain favorable terms from suppliers and even impact your business’s reputation.
Can I improve my business credit score if it’s currently low?
Absolutely! There are strategies to improve your business credit score. Focus on making timely payments, reducing debt, and establishing trade lines by working with suppliers who report to credit bureaus.
 Norfolk Publications Publications ORG in Norfolk!
Norfolk Publications Publications ORG in Norfolk!

