Small business charging credit card fees has become a prevalent issue, affecting profitability and growth. As technology evolves and payment processing becomes more sophisticated, the cost of accepting credit cards continues to rise for small businesses. This trend raises important questions about the financial implications of credit card fees and how small business owners can navigate this evolving landscape.
Understanding the various types of credit card fees, their calculation methods, and the factors influencing their cost is crucial for small business owners. From interchange fees to assessment fees, each type plays a role in the overall cost of accepting credit cards. Furthermore, negotiating lower processing rates can be a vital strategy for managing these expenses.
The Rise of Credit Card Fees for Small Businesses
The cost of accepting credit cards has become a significant concern for many small businesses. While credit cards have become a ubiquitous form of payment, the fees associated with processing them have steadily increased, putting a strain on already tight profit margins. Understanding the historical context, the impact of technology, and the key factors driving this trend is crucial for businesses to navigate this evolving landscape.
Historical Context of Credit Card Fees
Credit card fees have been a part of the payment processing landscape since the inception of credit cards. Initially, these fees were relatively low, reflecting the cost of processing transactions. However, as the credit card industry evolved and competition intensified, the fees began to rise. This rise was fueled by several factors, including:
- Increased Processing Costs: The cost of processing credit card transactions has increased over time due to factors such as enhanced security measures, fraud prevention, and the need to comply with evolving regulations.
- Interchange Fees: These are fees charged by card networks (Visa, Mastercard, etc.) to banks for processing transactions. These fees are a significant component of overall credit card processing costs and have been subject to ongoing debate and scrutiny.
- Competition and Market Dynamics: The competitive nature of the credit card industry has led to a dynamic where banks and card networks constantly seek to optimize their revenue streams. This has resulted in a gradual increase in interchange fees and other processing charges.
Impact of Evolving Payment Processing Technologies
The emergence of new payment processing technologies, such as mobile payments and online payment gateways, has had a mixed impact on credit card fees. While some technologies have led to cost reductions, others have created new opportunities for fee increases.
- Reduced Processing Costs: Some payment technologies, like mobile payments, have streamlined transaction processing, leading to potential cost savings. However, these savings have not always been passed on to merchants.
- New Fee Structures: The introduction of new payment methods, such as mobile wallets and digital currencies, has led to the creation of new fee structures and revenue models. This has created complexities for businesses trying to navigate the evolving payment landscape.
- Data-Driven Pricing: The increasing availability of data on consumer spending habits has enabled payment processors to implement more sophisticated pricing models. This can lead to personalized pricing based on factors such as transaction volume, industry, and customer demographics.
Factors Contributing to the Increase in Credit Card Fees
Several key factors have contributed to the increasing prevalence of credit card fees for small businesses. Understanding these factors is essential for businesses to develop strategies for managing their payment processing costs.
- Increased Consumer Demand for Credit Cards: The widespread adoption of credit cards has created a significant market for payment processors, leading to increased competition and pressure on merchants to accept credit cards.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations, such as the Durbin Amendment, which aimed to promote competition in the debit card market, have impacted the fee structure for credit card transactions.
- Growth of Online and Mobile Commerce: The rapid growth of online and mobile commerce has increased the reliance on credit card payments, further fueling the demand for payment processing services.
Understanding Credit Card Processing Fees
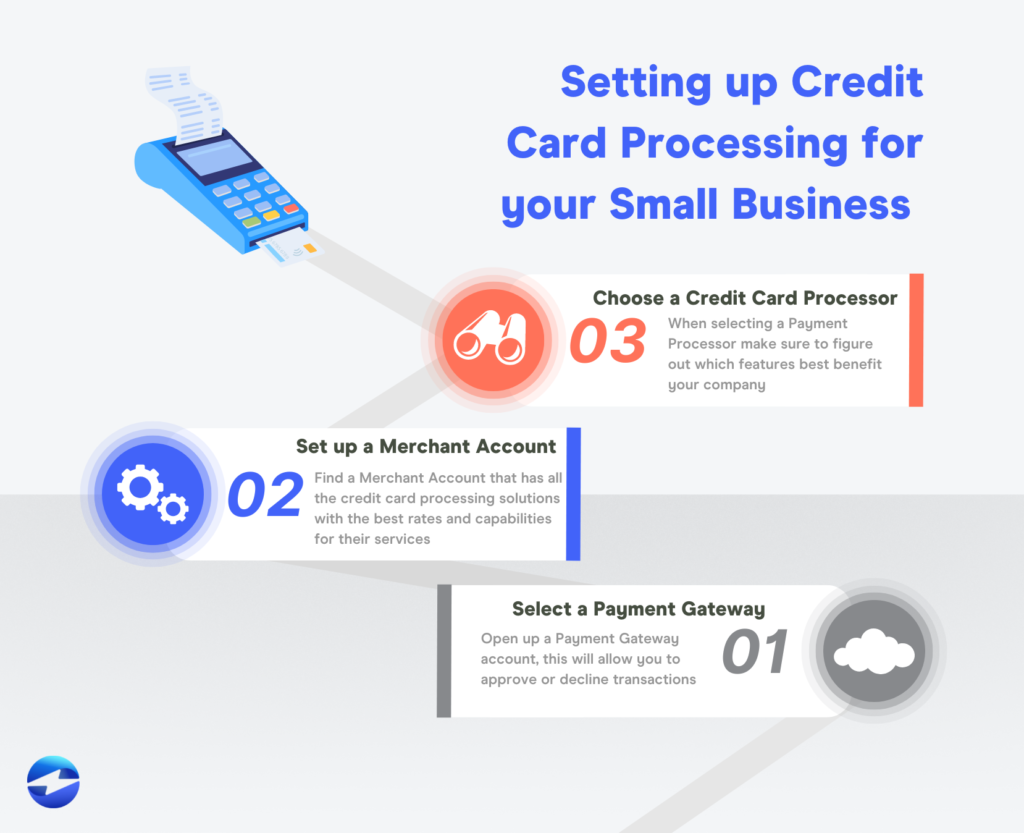
Navigating the world of credit card processing fees can be daunting for small business owners. These fees, often a hidden cost, can significantly impact your bottom line. Understanding the various types of fees, how they are calculated, and ways to negotiate lower rates is crucial for maximizing your profits.
Types of Credit Card Processing Fees
Credit card processing fees are categorized into several distinct types, each with its unique impact on your business.
- Interchange Fees: These are the largest component of credit card processing fees. They are set by the credit card networks (Visa, Mastercard, Discover, American Express) and represent the cost of transferring funds between the card issuer and the merchant. Interchange fees vary depending on the type of card (debit, credit, rewards), the transaction amount, and the cardholder’s industry.
- Assessment Fees: These fees are charged by the credit card networks for their services, including fraud prevention and data security. Assessment fees are typically a percentage of the transaction amount.
- Payment Gateway Fees: This fee is charged by the payment gateway, which acts as an intermediary between your business and the credit card processor. Payment gateway fees typically involve a monthly subscription fee and a per-transaction fee.
- Statement Fees: Some processors charge a monthly fee for issuing statements or providing other administrative services.
- Chargeback Fees: If a customer disputes a charge, you may be charged a fee to process the chargeback.
- Early Termination Fees: If you cancel your contract with a processor before the end of the term, you may be charged a fee.
Calculating Credit Card Processing Fees
The cost of credit card processing fees is determined by several factors, including:
- Interchange Rate: This is the largest component of the fee and varies based on the card type, transaction amount, and industry. For example, rewards cards typically have higher interchange rates than standard credit cards.
- Processor Markup: This is the profit margin that the credit card processor adds to the interchange rate. Processor markups can vary widely, so it’s essential to shop around for the best rates.
- Transaction Volume: Businesses with higher transaction volumes often receive lower processing rates.
- Payment Method: Different payment methods, such as swiped, keyed-in, or online transactions, have different processing fees.
Negotiating Lower Credit Card Processing Rates
While credit card processing fees are unavoidable, there are ways to negotiate lower rates:
- Shop Around: Compare rates from different processors and consider using a payment gateway that offers lower fees.
- Negotiate with Your Processor: If you have a high transaction volume or are willing to sign a long-term contract, you may be able to negotiate a lower rate with your current processor.
- Consider Alternative Payment Methods: Explore alternative payment methods, such as ACH payments or mobile wallets, which may have lower processing fees.
- Increase Average Transaction Value: By increasing the average transaction value, you can reduce the percentage of fees paid per transaction.
The Impact of Credit Card Fees on Small Businesses

Credit card fees are a significant expense for small businesses, impacting their profitability, pricing strategies, and overall growth. Understanding the implications of these fees is crucial for business owners to make informed decisions and navigate the financial landscape effectively.
Financial Implications of Credit Card Fees
Credit card fees directly impact a small business’s bottom line by reducing profits. These fees are typically calculated as a percentage of the transaction amount, known as the interchange fee, plus a fixed per-transaction fee. For example, a business might pay a 2% interchange fee and a $0.10 per-transaction fee for each credit card purchase. This means that for a $100 purchase, the business would pay $2 in interchange fees and $0.10 in transaction fees, resulting in a total fee of $2.10.
These fees can quickly add up, especially for businesses with high transaction volumes. Consider a small retail store processing $10,000 in credit card sales monthly. With a 2% interchange fee and a $0.10 per-transaction fee, the monthly credit card processing fees would amount to $210. This represents a significant portion of the business’s revenue, directly impacting its profitability.
Impact on Pricing Strategies and Customer Purchasing Decisions
Credit card fees can influence a small business’s pricing strategies. To offset the cost of these fees, businesses may consider raising prices, passing the cost on to customers. However, this can make their products or services less competitive, potentially discouraging customers from making purchases. Alternatively, businesses might choose to absorb the cost of credit card fees, impacting their profit margins.
“The impact of credit card fees on small businesses is significant. They can impact pricing strategies, customer purchasing decisions, and overall business profitability.”
Customers are often sensitive to price increases, and a business’s decision to raise prices to cover credit card fees could lead to a decrease in sales. This can be particularly challenging for businesses operating in competitive markets where price is a key factor in customer purchasing decisions.
Impact on Cash Flow and Business Growth
Credit card fees can also have a significant impact on a small business’s cash flow. When a customer makes a credit card purchase, the business does not receive the full amount of the sale immediately. Instead, the payment is processed through the credit card network, and the business receives the funds minus the processing fees after a delay, typically within a few business days. This delay in receiving funds can strain a business’s cash flow, particularly for businesses with limited working capital.
Furthermore, credit card fees can limit a business’s ability to invest in growth. The funds that are lost to credit card processing fees could be used for marketing, expanding operations, or hiring new employees. By reducing the available capital, these fees can hinder a business’s ability to grow and achieve its full potential.
Strategies for Managing Credit Card Fees: Small Business Charging Credit Card Fee
Credit card fees are an unavoidable cost for many small businesses. However, there are strategies that businesses can employ to minimize these fees and improve their bottom line. These strategies involve negotiating with payment processors, exploring alternative payment methods, and implementing operational efficiency measures.
Negotiation
Negotiating with your payment processor can be an effective way to reduce your credit card processing fees. Payment processors are often willing to negotiate rates, especially if you have a high volume of transactions or are willing to switch processors. Here are some key points to consider when negotiating:
- Review your current contract: Carefully examine your current contract with your payment processor. Look for opportunities to renegotiate fees, such as the interchange rate, monthly fees, or transaction fees.
- Compare rates from other processors: Contact several payment processors and compare their rates. This will give you a better understanding of the market and provide leverage when negotiating with your current processor.
- Negotiate volume discounts: If you process a high volume of transactions, you may be eligible for volume discounts.
- Bundle services: Payment processors often offer bundled services, such as payment gateways, virtual terminals, and recurring billing. By bundling services, you may be able to negotiate a lower overall rate.
Alternative Payment Methods
Offering alternative payment methods can reduce your reliance on credit cards and lower your overall processing costs. Here are some options:
- Debit cards: Debit cards generally have lower interchange rates than credit cards, leading to lower processing fees.
- ACH payments: ACH payments are electronic transfers from a bank account. They often have lower processing fees than credit cards, especially for recurring payments.
- Digital wallets: Digital wallets, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, can reduce processing fees and offer a more streamlined checkout experience for customers.
- Cash discounts: Offering a cash discount can encourage customers to pay with cash, which eliminates processing fees.
Operational Efficiency
Improving your operational efficiency can also help minimize credit card fees. Here are some strategies:
- Automate payments: Automating payments for recurring bills and subscriptions can reduce the number of manual transactions, which can lower your processing fees.
- Minimize chargebacks: Chargebacks are when a customer disputes a charge on their credit card. By implementing clear return policies and providing excellent customer service, you can minimize chargebacks, which can significantly impact your processing fees.
- Track your fees: Regularly track your credit card processing fees to identify areas where you can save. Compare your fees to industry benchmarks and look for opportunities to reduce costs.
The Future of Credit Card Fees for Small Businesses
The landscape of credit card processing fees for small businesses is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and changing consumer preferences. Understanding these trends is crucial for small business owners to navigate the future of payment processing and optimize their financial strategies.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
The emergence of new technologies is likely to significantly impact credit card processing fees for small businesses.
- Alternative Payment Methods: The growing popularity of digital wallets, mobile payment platforms, and buy now, pay later (BNPL) options could lead to new fee structures and processing models. These alternative payment methods often come with their own set of fees, which small businesses need to consider.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being increasingly used to detect fraud, optimize payment processing, and personalize customer experiences. These technologies can potentially reduce processing costs and increase efficiency, potentially leading to lower fees for small businesses.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize payment processing by offering a secure, transparent, and cost-effective alternative to traditional methods. While still in its early stages, blockchain could potentially disrupt the existing credit card processing ecosystem and lead to new fee structures.
Regulatory Changes and Their Influence
Regulatory changes can significantly impact the credit card processing landscape, affecting fees and the overall cost of accepting payments.
- Interchange Fees: Interchange fees, the fees charged by card networks (like Visa and Mastercard) to banks for processing transactions, are a major component of credit card processing costs. Regulatory scrutiny of interchange fees could lead to changes in their structure, potentially benefiting small businesses.
- Data Security Regulations: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) mandates specific security measures for businesses that process credit card payments. Compliance with these regulations can be costly, but regulatory changes aimed at simplifying compliance could potentially reduce these costs for small businesses.
- Antitrust Scrutiny: Increased antitrust scrutiny of card networks and payment processors could lead to greater competition and potentially lower fees for small businesses. This could create a more favorable environment for small businesses to negotiate better payment processing terms.
Opportunities and Challenges for Small Businesses, Small business charging credit card fee
The evolving landscape of credit card processing presents both opportunities and challenges for small businesses.
- Negotiating Lower Fees: Small businesses can leverage their bargaining power by exploring alternative payment processors and negotiating lower fees with existing providers. They can also consider bundling services to secure better rates.
- Adopting New Technologies: Embracing emerging technologies, such as AI-powered fraud detection and blockchain-based payment processing, can help small businesses optimize their payment processing operations and potentially reduce costs.
- Staying Informed: Small businesses need to stay informed about regulatory changes, technological advancements, and industry trends to navigate the evolving payment processing landscape effectively.
- Diversifying Payment Options: Offering a variety of payment options, including alternative payment methods like digital wallets and BNPL, can attract a wider customer base and enhance the customer experience.
Epilogue

Managing credit card fees effectively requires a proactive approach that encompasses negotiation, exploring alternative payment methods, and optimizing operational efficiency. While credit card fees present a challenge, small businesses can adopt strategies to minimize their impact and ensure sustainable growth. By staying informed about emerging trends and regulatory changes, small business owners can navigate the evolving landscape of credit card processing and make informed decisions to protect their financial well-being.
Clarifying Questions
What are the different types of credit card fees?
Common credit card fees include interchange fees, assessment fees, gateway fees, and statement fees. Each fee has a specific purpose and contributes to the overall cost of accepting credit cards.
How can I negotiate lower credit card processing rates?
Negotiating lower rates often involves comparing offers from different processors, highlighting your business volume, and seeking discounts for accepting debit cards or using specific payment terminals.
Are there alternative payment methods to reduce credit card fees?
Yes, consider offering alternative payment methods like cash, checks, ACH transfers, or digital wallets to encourage customers to use options with lower processing costs.
 Norfolk Publications Publications ORG in Norfolk!
Norfolk Publications Publications ORG in Norfolk!

